Chronic indications for hyperbaric oxygenation treatment
HBOT (hyperbaric oxygen therapy) is increasingly used and recommended by doctors to treat a variety of chronic conditions such as skin ulcers, some types of infections or aseptic bone necrosis. The latest scientific studies also demonstrate that hyperbaric oxygen therapy significantly improves neurocognitive function and symptoms of post-COVID.
In chronic conditions, hyperbaric oxygen therapy is often prescribed as a complement to other established treatments, as the high doses of pure oxygen in the hyperbaric environment make the healing and recovery process more efficient.
The effectiveness of hyperbaric oxygen therapy may vary depending on the condition in question and the individual patient's condition. Before listing the studied indications for HBOT in chronic conditions, it is important to note that hyperbaric oxygen therapy is not recommended in all cases of chronic conditions and you should discuss with your doctor whether this is the most appropriate treatment option.
Chronic infections with limited response to classical treatments
Some of the most common chronic infections that can be treated with hyperbaric therapy are osteomyelitis, osteitis, osteodiscitis, soft tissue infections (open wounds or burns), inner ear infections, lung infections, skin infections (abscesses or ulcers), and borreliosis. Because of the principle of operation, in addition to the chronic infections listed below, hyperbaric oxygen therapy can significantly improve the effectiveness of prescribed antibiotic treatment in the treatment of infections with polyresistant bacteria and intra-hospital infections as well as infections associated with immuno-depressive conditions (HIV).
- Osteomyelitis is an infection of the bone and can be caused by bacteria, fungi or other micro-organisms that enter the bone through injury, surgery or other routes. Studies show that when used as adjuvant treatment for refractory osteomyelitis (chronic osteomyelitis, that which does not respond or relapses after adequate treatment), hyperbaric therapy is associated with remission in about 85% of cases.
- Lyme disease is a bacterial infection caused by Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria, which is transmitted by tick bites and can cause symptoms such as skin rashes, muscle and joint pain, fever, sleep disturbances, difficulty concentrating, and headaches. If not treated in time, it can cause serious health problems. Recent studies show that hyperbaric oxygen therapy can be effective in reducing symptoms and improving quality of life in patients with Lyme disease, particularly in cases where the infection has caused neurological or cardiovascular problems.
- Chronic relapsing sinusitis is often caused by a bacterial or fungal infection and can be difficult to treat. This can cause permanent changes to the lining of the sinuses, which can lead to repeated sinusitis. HBOT can help improve blood circulation to the sinuses and help destroy bacteria and other microorganisms that cause sinus infections.
- Recurrent urinary tract infection is a urinary tract infection that can affect any part of the urinary system. In addition to recurrent urinary tract infection, recurrent prostatitis and adnexitis are two other conditions where hyperbaric oxygen therapy can successfully complement antibiotic treatment, especially in recurrent infections.
- Skin infections (erysipelas, pyoderma) are skin infections that can sometimes be difficult to treat, especially if poor circulation is a contributing factor. In addition to reducing inflammation and killing bacteria, hyperbaric oxygen therapy works by increasing the amount of oxygen that is delivered to the tissues and stimulating the growth of new blood vessels in the affected area, and this can significantly help improve the healing process.
- Aspergillosis is a fungal infection that can affect the respiratory tract but can also spread to other parts of the body and can cause infections of the skin, eyes and other organs. Aspergillosis is more common in people with compromised immune systems, such as those with HIV/AIDS, cancer or who have received organ transplants, but it can also affect healthy people. Medical studies show that HBOT treatment, applied in conjunction with antifungal treatment, significantly increases the healing and recovery process of aspergillosis.
- Periodontosis is a condition that causes inflammation of the tissue that supports and anchors teeth in the jawbone. Numerous inflammations and infections can occur in the gums, and in more advanced cases even pus pockets that destroy the soft tissue and damage the bone structure, which can lead to tooth loss. Recent studies demonstrate the effectiveness of combined treatment of hyperbaric oxygen therapy with FM-UD (ultrasonic subgingival debridement) for the treatment of moderate to severe periodontitis.
Chronic peripheral ischaemia
The condition involves a reduction in blood flow to the arms and legs due to narrowed or blocked arteries. Hyperoxia triggered by hyperbaric therapy produces a number of physiological effects that have numerous proven benefits. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is effective and used as an important adjunct treatment in correcting ischemia and hypoxia caused by chronic peripheral ischemia, promoting microcirculation, reducing inflammation and acting directly on possible infections and accelerating wound healing.
The efficacy of hyperbaric oxygen therapy as an adjuvant treatment is proven by clinical studies in conditions such as arteritis, thrombophlebitis, microangiopathy or ischemic heart disease.
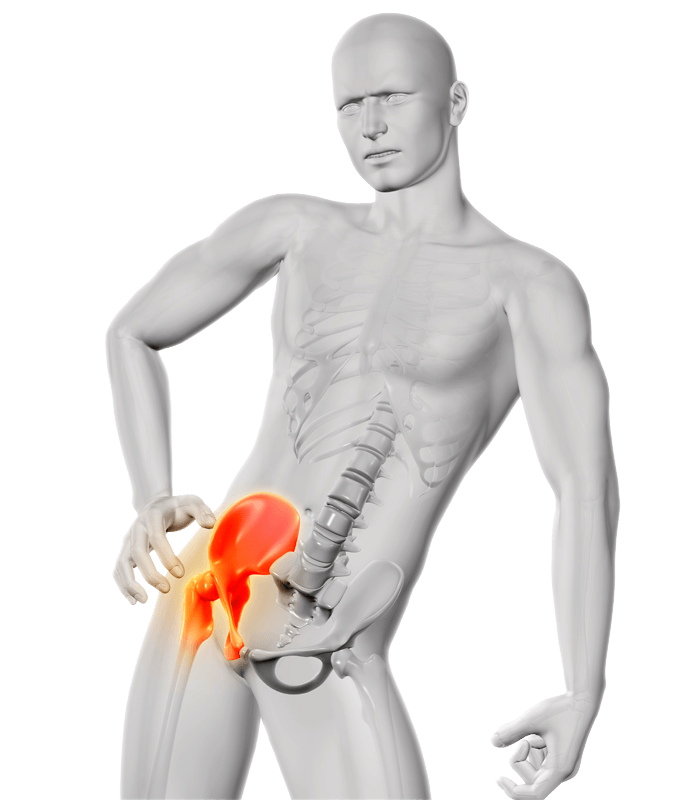
Aseptic bone necrosis
Aseptic bone necrosis (or avascular bone necrosis) is a disease in which bone tissue is destroyed without being caused by infection. Aseptic bone necrosis is more common in the upper part of the thigh bone (femoral head). This occurs when the hip no longer gets the amount of blood it needs to function properly. Hip bones need vascularisation, and without it, the bone in the femoral head begins to deteriorate and die, leading to the femoral head collapse.
If the disease is discovered in relatively early stages, aseptic femoral head necrosis can be successfully treated with hyperbaric oxygen therapy, avoiding complex procedures such as hip joint replacement. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) helps treat aseptic necrosis by increasing blood flow to the affected bones and promoting bone tissue regeneration. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy is now increasingly recommended by orthopaedic physicians to halt the progression of avascular bone necrosis and prevent the onset of coxarthrosis (hip arthrosis).
Anti-tumour treatment in combination with radiotherapy/chemotherapy
Studies show that hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) given in combination with radiotherapy or chemotherapy can lead to a significant reduction in mortality and recurrence. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy may be beneficial in treating cancer through several mechanisms.
Improving the ability of radiotherapy and chemotherapy to kill cancer cells: HBOT can improve the ability of radiotherapy and chemotherapy to kill cancer cells, especially hypoxic cancer cells (cells that are low in oxygen).
Reducing inflammation: HBOT can help reduce inflammation in the body, which can be beneficial in cancer, as chronic inflammation can contribute to the development and progression of cancer.
Strengthening the immune system: HBOT can boost the immune system and increase the production of immune cells, which can help the body fight cancer.
Reducing the side effects of cancer treatment: HBOT can help reduce the side effects of cancer treatment, such as nausea, vomiting and fatigue.
Osteoradionecrosis
Osteoradionecrosis (ORN) is a common complication of radiation in cancer patients. It can occur in patients who have had radiotherapy for cancer in the head or neck area. Osteoradionecrosis can also develop months or years after radiotherapy and usually occurs in the lower jaw (mandible). Symptoms include pain in the mouth, swelling of the jaw and difficulty opening the mouth fully. Recent studies show that hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) can improve and accelerate wound healing in patients with stage 1 and 2 ORN and reduce the risk of surgery.
Radiation ulcers
Radiotherapy can be a lifesaving method for diseases such as cancer, and advances in the field are making it safer and reducing radiation damage. However, radiation can sometimes cause side effects such as skin ulcers. This is an advanced adverse reaction that can affect skin, tissue or even bone. These ulcers can be difficult to treat due to ongoing radiation to the ulcer area and the body's reduced ability to heal wounds during the illness.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has been studied and recommended by the oncology department of the renowned UCLA Medical Center in the US as a treatment for radiation-induced ulcers because of its ability to increase blood flow to the affected area and improve tissue oxygenation. HBOT can also stimulate the growth of new blood vessels and help reduce inflammation. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has also proven effective in treating other late side effects of radiotherapy, such as cystitis, radicular rectitis or radicular ileitis.
Diabetes
HBOT is a highly effective adjuvant treatment for diabetic complications such as diabetic foot ulcer, diabetic neuropathy, diabetic retinopathy or diabetic microangiopathy.
In diabetic foot ulcers, hyperbaric oxygen therapy is recommended by the FDA and UHMS, with the therapy recognized to accelerate the healing process, significantly reduce amputation rates and risk, and improve patient quality of life.
Diabetic neuropathy is a complication of diabetes that is characterised by nerve damage and can affect different parts of the body, including the hands, feet and internal organs. This can lead to symptoms such as numbness, tingling, pain, muscle weakness and coordination problems. Dozens of studies recommend hyperbaric oxygen therapy to treat diabetic neuropathy as well as diabetic retinopathy and diabetic microangiopathy, working by increasing blood flow and oxygen levels to affected tissues, which can accelerate the healing process and improve symptoms.
A study organised by Portugal's National Centre for Chronic Diseases (CEDOC) shows that HBOT can improve glucose tolerance in diabetic patients and suggests that HBOT could also be used as a therapeutic intervention for type 2 diabetes.
Disturbances in perception
Tinnitus, migraine, vertigo or smell and taste disorders are conditions successfully studied in the field of hyperbaric therapy, with HBOT being recommended as an adjuvant treatment, especially at onset and in the early stages.
Inflammatory bowel diseases
Ulcerative colitis
Ulcerative colitis is a chronic inflammatory condition of the colon (large intestine) that can cause abdominal pain, diarrhoea, blood in the stool and fatigue. It is characterised by the appearance of ulcers in the lining of the colon.
While traditional treatments based on corticosteroids, anti-inflammatories and immunomodulators can produce serious long-term side effects, hyperbaric oxygen offers a promising new treatment option as it targets both tissue hypoxia and inflammation with very few side effects. Recent studies evaluating the impact of hyperbaric oxygen treatment in acute ulcerative colitis attacks have shown very good results after 40 sessions of hyperbaric therapy. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy stimulates colonic stem cells, induces mucosal healing and accelerates the reduction of inflammation.
Crohn's disease
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can help reduce the severity of symptoms experienced by patients with Crohn's disease and improve their quality of life.
Also, in numerous studies, hyperbaric therapy has been associated with significantly higher cure rates in Crohn's disease complications such as perianal Crohn's disease, enterocutaneous fistula or pyoderma gangrenosum.
Adjuvant recuperative treatment
Together with physiotherapy and physiotherapy sessions, hyperbaric therapy is an excellent adjuvant rehabilitative treatment in paresis and spastic folds. Thanks to HBOT's working mechanism, symptoms can be relieved more quickly and effectively.
Autism
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) is the subject of more and more studies for autism and is recommended as an adjunctive treatment, part of a multidisciplinary therapeutic plan that may include psychotherapy, drug treatment and other therapies such as speech therapy, occupational therapy or restrictive diet.
Benefits of HBOT in the treatment of autism may include improved language, awareness, behaviour and increased socialization by affecting pathophysiological findings.
Symptomatic pain treatment
Through the mechanism of reducing inflammation in the body, oxygen therapy can also be used successfully in the symptomatic treatment of pain caused by migraines, various arthroses, shingles, fibromyalgia, Tarlov cyst, disc disease, and chronic fatigue syndrome.
Post COVID-19 or Long COVID syndrome
Although the post-COVID syndrome is not yet fully defined, the predominant symptoms reported include shortness of breath, headache, angina-like chest pain, abdominal pain, muscle pain, fatigue, cognitive problems or anxiety and depression. The severity and duration of these symptoms can vary greatly from person to person.
According to recent studies in the UK and Israel, patients with Post COVID-19 symptoms who underwent hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) showed significant improvement in cognitive, neurological and psychiatric function compared to a control group. The protocol consisted of 40 daily sessions of hyperbaric oxygen therapy at a pressure of 2 absolute atmospheres (ATA) for 90 minutes, with oxygen fluctuations every 20 minutes, during which patients breathed 100% pure oxygen.
Other chronic conditions
With 14 FDA-approved conditions, over 30 conditions approved by the European Committee for Hyperbaric Medicine (ECHM), and hundreds of completed and ongoing clinical trials, the scientific community continues to explore potential benefits for dozens of major conditions.
To find out more details about the most important scientific studies in the field of hyperbaric medicine, visit this section: Scientific references
Safety and effectiveness of HBOT
The information provided by the FDA as well as numerous studies show that when applied properly, in accredited medical centers, hyperbaric therapy can be considered one of the safest medical treatments available.
To safely benefit from the studied effects of hyperbaric oxygen therapy it is important to ensure at least three things:
- The hyperbaric chamber is medically accredited and operated by certified personnel according to the regulations in force.
- The pressure in the chamber can reach 3 ATA. (ATA pressure is composed of the value of the atmospheric pressure 1 bar + the value of the additional pressure in the hyperbaric chamber)
- Oxygen inspired during therapy must have a purity greater than 99.5%. For more technical details but also for information on the different types of hyperbaric chambers, click here: Medical HBOT or mild HBOT chambers?
The European Commission of Hyperbaric Medicine also divides the conditions in which hyperbaric oxygen therapy is recommended into 3 categories:
| Grade 1: Strict recommendation | Grade 2: Recommended | Grade 3: Optional | Other indications: |
|---|---|---|---|
|
|
|
|
| Grade 1: Strict recommendation |
|---|
|
| Grade 2: Recommended |
|---|
|
| Grade 3: Optional |
|---|
|
| Other indications: |
|---|
|