Article reviewed by: Dr. Sturz Ciprian, Dr. Tîlvescu Cătălin and Dr. Alina Vasile
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy: From Military Applications to Civilian Uses
- Origins and Military Applications
- Expansion of Uses in Military Structures
- Transition to Civilian Uses
- Uses in Sports and Recovery
- Modern Uses in Military and Emergency Structures
- Conclusion
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy (HBOT) has evolved significantly over time, transitioning from its initial military uses to a wide range of civilian applications. This article explores the origins of HBOT, its uses within military forces, and how it has been adopted in the civilian sector, with concrete examples illustrating the effectiveness of this therapy.

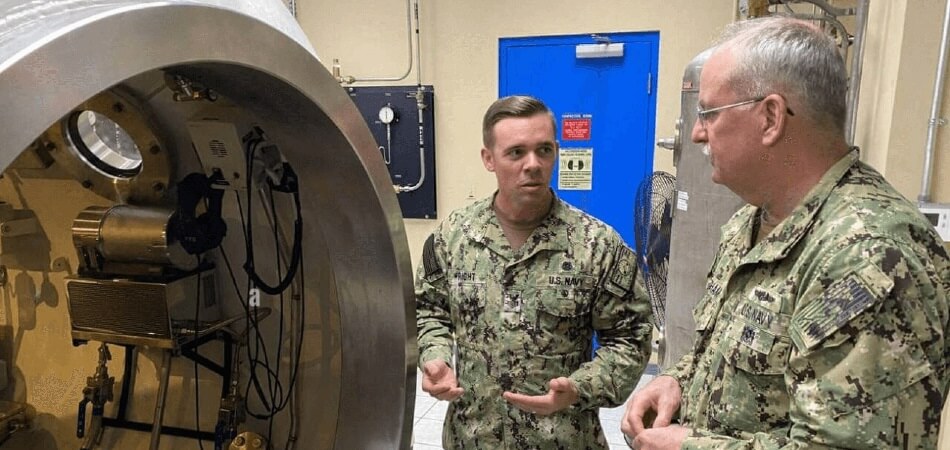
Origins and Military Applications
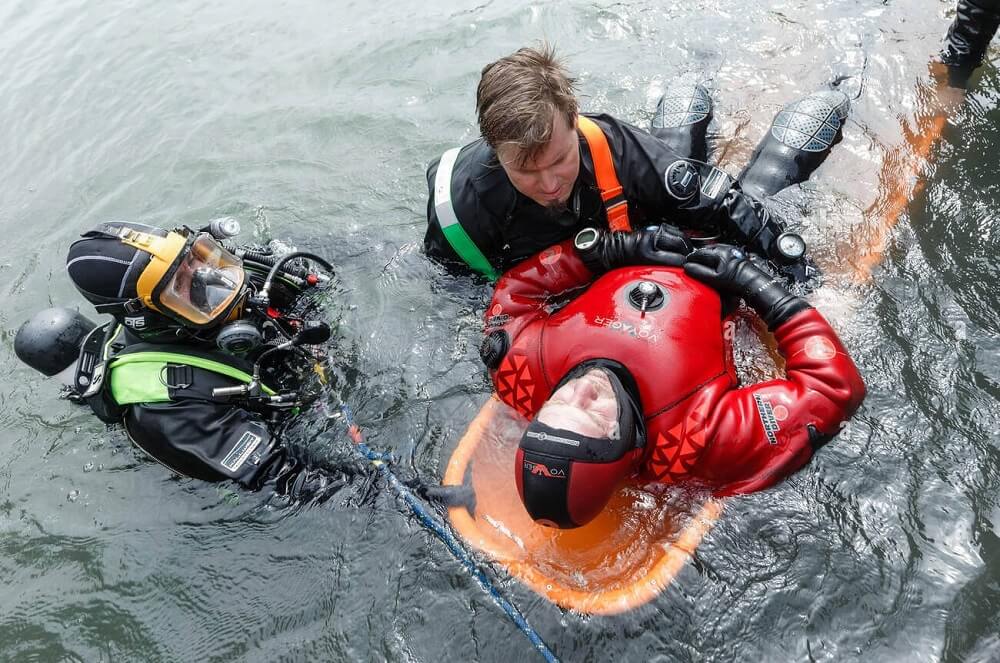
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy was initially developed to treat decompression sickness in military divers. Decompression sickness occurs when divers ascend too quickly, causing gas bubbles to form in the blood and tissues. In the 1940s, the United States Navy and later NATO forces began using hyperbaric chambers to treat these conditions. For example, during NATO military exercises in the North Sea in the 1960s, NATO divers frequently used hyperbaric chambers to treat cases of decompression sickness, preventing severe accidents and saving the lives of divers.
Expansion of Uses in Military Structures
Over time, hyperbaric therapy found applications in other areas of military medicine:
- Treatment of War Injuries: During the Vietnam War, military doctors used HBOT to treat complex wounds and severe infections, aiding in faster healing and reducing infections. A notable case was that of a soldier severely injured by an explosion who benefited from hyperbaric therapy to recover more quickly.
- Carbon Monoxide Poisoning: During rescue operations in sunken submarines, such as the Kursk submarine incident, hyperbaric therapy was crucial for treating crew members exposed to dangerous levels of carbon monoxide.
- Recovery from Intense Training: Soldiers at Fort Bragg military base used hyperbaric chambers to accelerate muscle recovery and reduce inflammation after intense training, allowing them to return more quickly to full operational capacity.
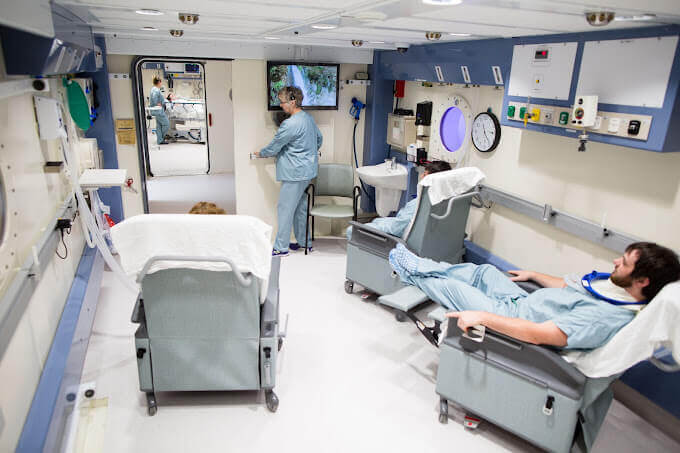
Transition to Civilian Uses
Starting in the 1960s, HBOT was introduced into the civilian medical field. Doctors began to recognize the benefits of this therapy in treating various conditions:
- Chronic Wounds and Diabetic Ulcers: Between 1980 and 1990, clinical trials conducted by the renowned Mayo Clinic showed significant improvements in patients with diabetic ulcers after hyperbaric oxygen therapy, reducing the risk of amputations. These positive results were published in various medical studies and contributed to the growing popularity of hyperbaric therapy as a standard treatment for diabetic ulcers in many other medical centers worldwide.
- Severe Burns: Following the 1987 King's Cross subway station fire in London, victims with severe burns benefited from hyperbaric oxygen therapy to accelerate the healing process and reduce the risk of infection. This tragic incident prompted authorities and the medical community to utilize hyperbaric therapy even more, as part of the treatment for fire victims, demonstrating the therapy's effectiveness in managing severe burns and other injuries resulting from such disasters.
- Necrotizing Infections: At Massachusetts General Hospital, a 10-year study showed that patients with necrotizing fasciitis treated in hyperbaric chambers had significantly better outcomes in terms of survival and reduced need for amputation. Hyperbaric therapy was successfully used to treat patients with necrotizing fasciitis, a severe infection that can lead to limb loss or even death.
Uses in Sports and Recovery
In addition to medical applications, hyperbaric therapy has been adopted in the sports field to accelerate recovery after intense training and injuries. For example, American football player Joe Namath used HBOT to recover from multiple concussions, reporting significant improvements in cognitive functions and overall health.
Modern Uses in Military and Emergency Structures
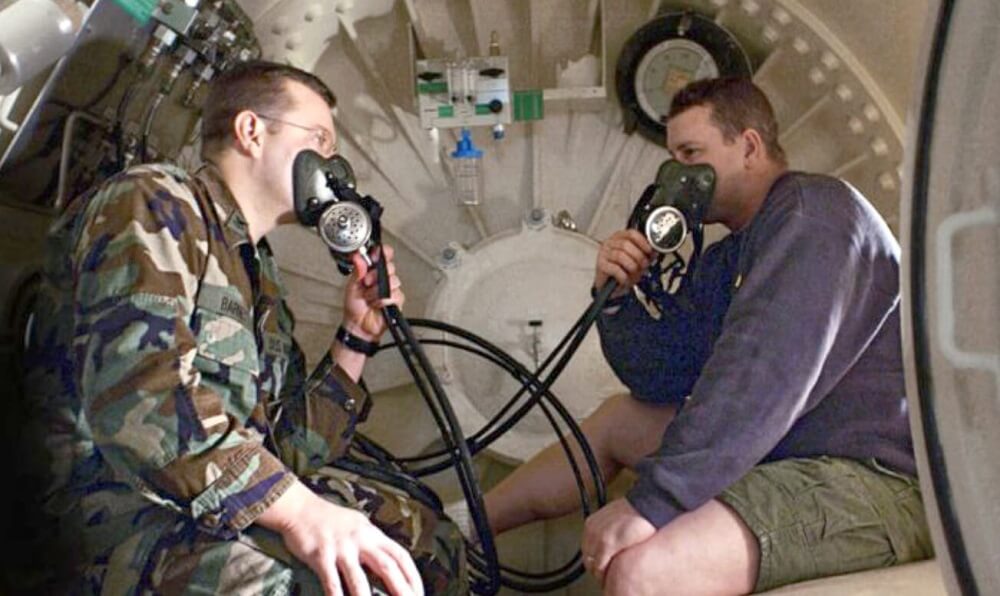
Armed Forces and NATO
The armed forces continue to use HBOT to treat war injuries, decompression sickness, and other medical conditions. Within NATO, hyperbaric chambers are standardized and integrated into treatment protocols for various emergency situations. For example, during missions in Afghanistan, injured soldiers were evacuated to NATO bases where HBOT was used to treat severe injuries and accelerate recovery.
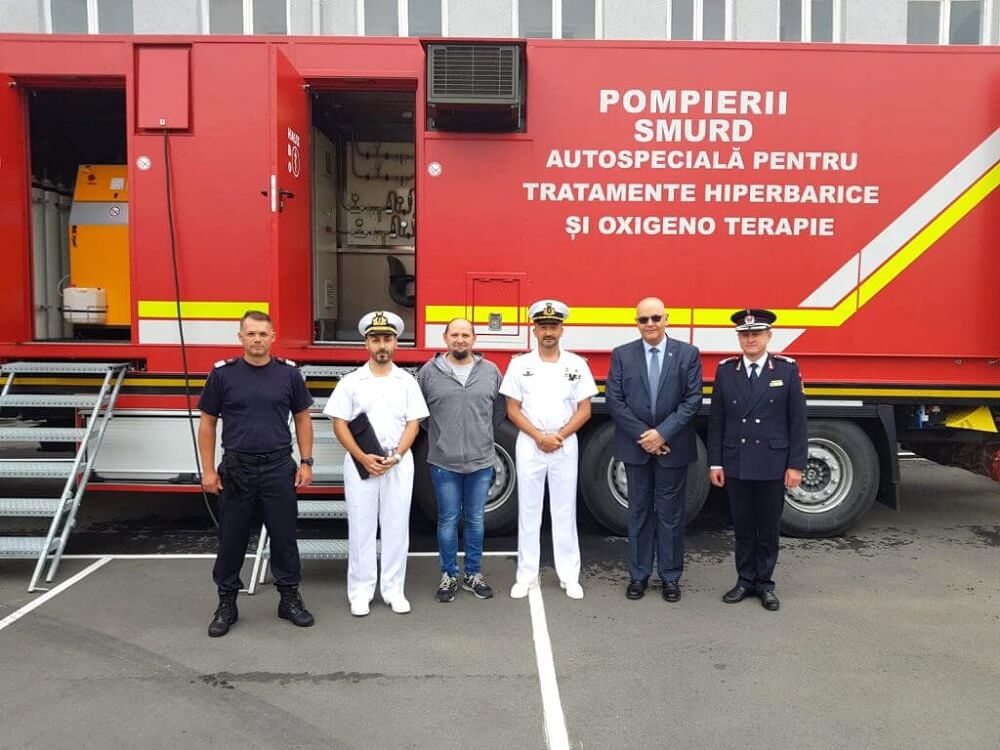

Firefighters and Police
Firefighters use hyperbaric chambers to treat carbon monoxide poisoning and other toxic smoke exposures. For example, after the devastating fire at the Colectiv club in Bucharest, some smoke-intoxicated victims
were treated with hyperbaric oxygen to rapidly remove toxins from the body. Following the incident, only a portion of the victims could be properly treated with hyperbaric therapy due to the limited number of
available seats. This situation highlighted the need for additional resources, and as a result, four mobile hyperbaric chambers were acquired to improve intervention capacity in future emergencies.
Additionally, police officers and other law enforcement agencies now benefit from this therapy in cases of exposure to hazardous chemicals or after severe injuries.
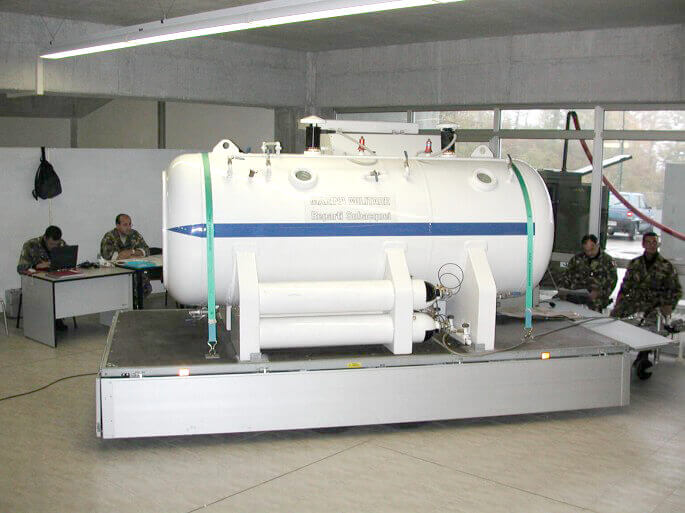

Rescue and Emergency Response Teams
In many countries, rescue and emergency response teams use hyperbaric therapy to treat victims of severe accidents and natural disasters. For example, after the 2010 Haiti earthquake, international rescue teams used mobile hyperbaric chambers to treat victims with severe injuries, thus accelerating the healing process and saving lives.
Conclusion
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy has evolved from its initial military uses to a wide range of applications in the civilian field. The benefits of this therapy are recognized in various medical and emergency fields, demonstrating its effectiveness in treating serious and complex conditions.
As technology and research in hyperbaric therapy advance, it is anticipated that this therapy will play an increasingly important role in modern medicine. Hyperbaric therapy will be essential not only in emergency interventions but also in treating chronic conditions, thus contributing to improving patients' quality of life and accelerating the healing process.




