Article reviewed by: Dr. Sturz Ciprian, Dr. Tîlvescu Cătălin and Dr. Alina Vasile
Lyme Disease (Borreliosis) - What It Is, Causes, Symptoms, and Treatment
- What is Lyme Disease (Borreliosis)?
- What causes Lyme disease and how is it transmitted?
- Is Lyme disease contagious?
- How to remove a tick and what to do if bitten?
- What are the symptoms and how does Lyme disease manifest?
- What are the risk factors for Lyme disease?
- How is Lyme disease diagnosed?
- What are the treatments for Lyme disease?
- What are the complications that can arise from Lyme disease?
- Who treats Lyme disease?
- How well is Lyme disease diagnosed?
- Prevention methods for Lyme disease?
- Conclusion
What is Lyme Disease (Borreliosis)?
Lyme disease, also known as borreliosis, is an infection caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi, transmitted to humans through the bite of an infected tick. Initial symptoms usually include a characteristic rash around the bite, fever, headache, and fatigue. If left untreated, the infection can affect the joints, heart, and nervous system.
Lyme disease is also referred to as Lyme infection or Lyme borreliosis, both representing different aspects of the same condition. The term "Lyme infection" emphasizes the infectious nature of the disease, while "Lyme borreliosis" highlights the specific pathogen, Borrelia burgdorferi. Regardless of the term used, prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent severe complications.
The term "Lyme" originates from the town of Lyme in Connecticut, USA, where the disease was first identified in the mid-1970s. Several children and adults in this area began to exhibit similar symptoms, leading to the discovery of the disease through medical investigations.
What causes Lyme disease and how is it transmitted?
Lyme disease is caused by the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi and, less commonly, other species of Borrelia, such as Borrelia mayonii. This bacterium is transmitted to humans through the bite of infected ticks, particularly ticks of the Ixodes genus, also known as deer ticks or black-legged ticks.
Transmission Mechanism:
- Tick Bite: The tick attaches to the host's skin (human or animal) to feed on blood. If the tick is infected with Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacteria can be transmitted into the host's bloodstream during feeding.
- Duration of Attachment: The risk of infection significantly increases if the tick remains attached to the skin for 36-48 hours or more. Removing the tick within the first 24 hours can greatly reduce the risk of disease transmission (CDC).
Not all ticks are infected with the bacterium Borrelia burgdorferi. The percentage of infected ticks varies significantly by region and species. For example, in some areas of the US, such as the southeastern United States, Ixodes scapularis (deer ticks) are rarely infected, while in other areas, the percentage can be as high as 50% (CDC). In the Netherlands, a study showed that approximately 14.7% of tested ticks were positive for Borrelia burgdorferi (BioMed Central).
In Romania, data on Lyme disease are monitored by the National Center for Surveillance and Control of Communicable Diseases (CNSCBT). Here, the incidence of Lyme disease varies by region and season, with a higher number of cases reported during the summer months when tick activity is at its peak.
For example, in 2022, 850 suspected cases of Lyme disease were reported. The number of confirmed cases represented 59% of the total number of cases entered into the national surveillance system.
The total number of reportable cases to the CNSSP (526) was 31% higher than the average for the 5 pre-pandemic years. The highest incidence rate was recorded in Sibiu County, followed by Maramureș County, with much higher numbers compared to other counties.
Is Lyme Disease Contagious?
No, Lyme disease is not contagious. It is not transmitted from person to person through direct contact, kissing, touching, or other forms of usual human contact. Infection with Borrelia burgdorferi, the bacterium that causes Lyme disease, occurs exclusively through the bite of infected ticks. Studies exploring other modes of transmission, including sexual transmission, have not yet provided conclusive results supporting this hypothesis.
How to Remove a Tick and What to Do If You’ve Been Bitten?
First, you should consult a doctor for tick removal and to receive appropriate recommendations. Avoid methods such as using oil, petroleum jelly, alcohol, or fire for tick removal, as these can cause the tick to release more infected fluids. If a doctor is not available, follow these steps:
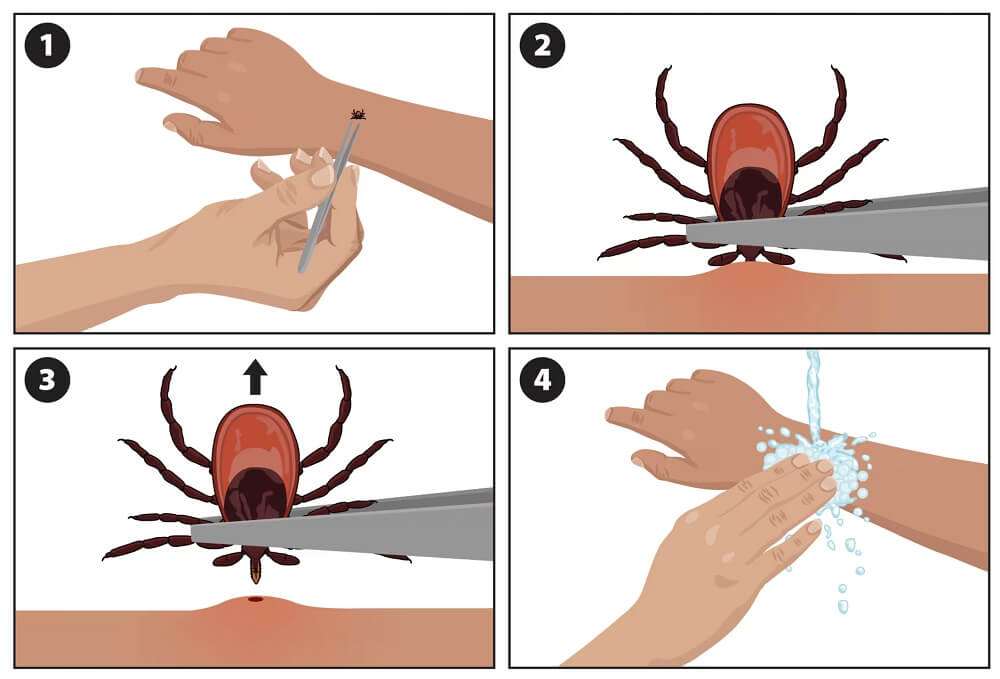
1. Removing the Tick:
- Prepare the Equipment: You need fine-tipped tweezers.
- Grab the tick: Use the tweezers to grasp the tick as close to the skin as possible without squeezing the tick's body.
- Pull Gently but Firmly: Pull slowly and steadily, without twisting or jerking. Avoid crushing the tick, as this may release infected fluids into your bloodstream.
- Clean the Bite Area: After removing the tick, clean the bite area and your hands with soap and water, and use antiseptic alcohol.
- Store the Tick: Keep the tick in a sealed container for potential future laboratory testing.
2. After Tick Removal:
- Consult a Doctor: If you notice any unusual symptoms such as rashes, fever, headaches, fatigue, or muscle pain, consult a doctor. These could be signs of Lyme disease or other tick-borne infections.
- Monitor the Bite Area: Check the bite site daily for a few weeks for signs of infection or rash.
- Additional Precautions: Do not use methods such as oil, petroleum jelly, alcohol, or fire to remove the tick, as these methods can cause the tick to release more infected fluids.
Proper and prompt removal of the tick and careful monitoring after the bite are essential for preventing complications. If any part of the tick (such as the head or mouthparts) remains in the skin, do not attempt to remove it with a needle or other sharp object, as this may worsen the wound and increase the risk of infection.
It is best to consult a doctor for complete tick removal and to receive appropriate recommendations.
What Are the Symptoms and How Does Lyme Disease Manifest?
Lyme disease presents a variety of symptoms, which can vary depending on the stage of the infection. The symptoms are divided into three main stages: early, disseminated, and persistent.
Early Stage Symptoms (3-30 days after tick bite):
- erythema migrans: A characteristic rash that occurs in approximately 70-80% of infected individuals. It starts as a small red spot at the bite site, gradually expands, and can grow up to 30 cm in diameter. The rash may have a "bull's-eye" appearance and is usually not painful or itchy.
- Flu-like Symptoms: Fever, chills, headaches, fatigue, muscle and joint aches, and swollen lymph nodes.
Disseminated Stage Symptoms (days to months after tick bite):
- Severe headaches and neck stiffness.
- Additional rashes: Rashes similar to erythema migrans but smaller.
- Facial paralysis (Bell's palsy).
- Arthritis with severe joint pain and inflammation, especially in the knees and other large joints.
- Palpitations and irregular heartbeat (Lyme carditis).
- Episodes of dizziness or difficulty breathing.
- Inflammation of the brain and spinal cord.
- Nerve pain and burning or tingling sensations in the hands and feet.
Persistent Stage Symptoms (months to years after tick bite):
- Chronic arthritis: Severe pain and inflammation, especially in the knees.
- Neurological problems: Encephalopathy, peripheral neuropathy, difficulty concentrating and with memory.
What Are the Risk Factors for Lyme Disease?
Main Risk Factors:
-
1. Geographic Location:
- People living in or spending time in areas known for tick prevalence.
- In Europe, the risk is higher in wooded and densely vegetated areas.
- In Romania, the risk is increased in Sibiu and Maramureș counties, as significantly more Lyme disease cases have been reported here compared to other counties.
- People working outdoors, such as farmers, foresters, gardeners, and construction workers, have an increased risk of exposure to infected ticks due to the nature of their work.
-
2. Outdoor Activities:
- People engaging in outdoor activities such as hiking, camping, gardening, or hunting have a higher risk of being bitten by infected ticks.
-
3. Inappropriate Clothing:
- Skin exposure, such as wearing short or inadequately covered clothing, can increase the risk of tick bites.
-
4. Pets:
- Pets spending time outdoors can bring ticks into the home, thereby exposing family members to risk.
-
5. Season:
- Tick activity is highest during the spring and summer months, so the risk of contracting Lyme disease is greater during these periods.
How is Lyme Disease Diagnosed?
Diagnosing Lyme disease involves a combination of clinical evaluation and laboratory tests to confirm the infection. The doctor uses information about symptoms and exposure history, along with specific blood tests and other analyses to establish the correct diagnosis. Here is how the process is carried out:
1. Clinical Evaluation
Medical History and Symptoms:
- The doctor will ask about your symptoms: For example, if you have experienced fever, headaches, fatigue, muscle and joint pain, or swollen lymph nodes.
- Questions about recent activities: Whether you have been in areas known for Lyme disease cases, such as forests or tall grass areas, and if you have been bitten by ticks.
Physical Examination:
- Checking for erythema migrans: This is a characteristic rash that appears around the tick bite, often having a "bull's-eye" appearance (a red spot with a clear center).
- Other physical signs: The doctor will look for other symptoms such as joint inflammation, facial paralysis (Bell's palsy), and signs of infection.
2. Laboratory Tests
Serological Tests:
-
ELISA Test (Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay):
- Purpose: Detects antibodies produced by the immune system against the Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria.
- How it works: A blood sample is taken and analyzed for the presence of specific antibodies. If the result is positive or inconclusive, the next test is performed for confirmation.
-
Western Blot Test:
- Purpose: Confirms the results of the ELISA test.
- How it works: Proteins from Borrelia burgdorferi are separated and their reaction with the patient’s antibodies is checked. It is more specific and helps eliminate false positive results.
Molecular Tests:
-
PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction):
- Purpose: Detects the bacteria's DNA in synovial fluid (from joints) or cerebrospinal fluid (from around the brain and spinal cord).
- How it works: Useful mainly in cases of Lyme arthritis or neuroborreliosis, but it is not commonly used because blood contains few bacteria, which can lead to false negative results.
Since ticks can transmit other diseases, doctors may perform additional tests to detect other pathogens, such as Anaplasma, Babesia, or Powassan virus.
The cost of these confirmatory tests varies between approximately €28 and €100, depending on the chosen laboratory and the type of test required. In Romania, laboratories that conduct PCR molecular tests for detecting Borrelia include Borrelia Centrum (Borrelia Centrum) in Bucharest, Bioclinica, Synevo, and MedLife, with Borrelia Centrum standing out for its more advanced and varied range of analyses in the field, being a specialized laboratory in such investigations.
What are the treatments for Lyme Disease?
Treatment for Lyme disease involves the use of antibiotics and other therapies to eliminate the Borrelia burgdorferi bacteria from the body and to manage symptoms and associated complications.
Before presenting the main treatment options for each stage of Lyme disease, we invite you to watch a short video where Dr. Csep Andrei explains the stages of the disease.
Treatments for Early Stages of Lyme Disease:
- Doxycycline: Frequently used for adults and children over 8 years old, administered for 10-21 days.
- Amoxicillin: Preferred for younger children, pregnant women, and those who cannot take doxycycline. Treatment lasts between 14 and 21 days.
- Cefuroxime: Alternative for those allergic to penicillins, administered for 14-21 days.
Treatment for Advanced Stages of Lyme Disease:
- Intravenous Antibiotics: In severe cases, especially when the disease affects the central nervous system, ceftriaxone or cefotaxime is used for 14-28 days.
- Symptomatic Treatment: Anti-inflammatory medications to control pain and joint inflammation, as well as medications for neurological symptoms.
Hyperbaric Oxygen Therapy - A Revolutionary Approach:
Lyme disease is difficult to treat, most often requiring prolonged courses of high-dose antibiotics. Recent studies show that
hyperbaric therapy may offer an alternative treatment and a very effective adjunctive treatment for Lyme disease, especially in refractory cases. Hyperbaric
therapy involves inhaling pure oxygen in a specially pressurized chamber.
The use of hyperbaric oxygen therapy has become increasingly popular worldwide for treating chronic forms of Lyme disease, as this method relies on oxygen penetrating the spaces between cells and into tissues
that are generally poorly oxygenated and affected by the disease. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy creates a hostile environment for the survival of Borrelia due to its bactericidal and bacteriostatic effects, working
synergistically with antibiotic treatment and other integrative therapies. Thus, the life cycle of this bacterium is interrupted because it cannot survive under such conditions.
The increased level of oxygen in the blood helps in healing affected tissues and combating bacterial infections, including Borrelia burgdorferi. Hyperbaric oxygen reduces inflammation and can help
relieve pain and discomfort in joints and muscles. There is evidence that hyperbaric therapy may aid in neurological function recovery affected by Lyme disease, improving symptoms such as
neuropathic pain, numbness, and cognitive difficulties.
A study conducted by Dr. William Fife at Texas A&M University showed that hyperbaric
oxygen therapy can bring significant improvements in Lyme disease treatment, especially for patients with persistent symptoms. 91 Lyme disease patients were treated at Texas A&M, with 75 completing HBOT
treatment, receiving between 40 and 120 sessions of hyperbaric oxygen therapy. All patients, except for 7, experienced significant improvement or complete resolution of symptoms, with lasting effects ranging
from three months to six years. Although further studies are needed, there is a possibility that, being a microaerophilic organism, the Borrelia burgdorferi spirochete might be eradicated through hyperbaric
oxygen therapy. With treatment duration ranging from 40 to 120 sessions in the study, only a small number of patients did not experience significant improvements. There is a fairly good chance that with a
sufficiently long treatment duration, most patients may achieve complete resolution of positive Lyme disease symptoms.
To fully understand hyperbaric therapy and its effectiveness in Lyme disease, we invite you to read this comprehensive guide. You will find answers to all your
questions, details about the entire process, as well as information about costs.
Hyperbarium Clinic is one of the most advanced and modern hyperbaric medicine centers in Romania, also specializing in treating Lyme disease. The entire staff is trained and certified
according to European standards, and the clinic's doctors have expertise in hyperbaric medicine. The medical director of the clinic is Dr. Ciprian Sturz, a general surgeon specialized in general, visceral, and
emergency surgery, with 15 years of experience in Germany.
As part of a series of free events organized by Hyperbarium Clinic, the event held in June 2024 brought together professionals and experts in infectious diseases and neurology to discuss and share innovative
and effective treatment strategies for Lyme disease. Presentations covered advances in medical research, symptom management, and the integration of new technologies and treatments into clinical practice. You
can watch a short summary of the event below.
If you have symptoms of Lyme disease or persistent symptoms after treatment, we encourage you to schedule a consultation to explore treatment options that not only can significantly improve your quality of life but also may lead to complete healing.
Post-Treatment Symptom Management:
- Post-Lyme Syndrome: Some individuals continue to experience symptoms such as fatigue, pain, and cognitive difficulties after antibiotic treatment. These cases may require additional therapies to manage symptoms. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy can help reduce inflammation, improve tissue oxygenation, and recover neurological functions, providing significant relief for patients with post-Lyme syndrome.
- Rehabilitation: Physical and occupational therapy can aid in the recovery of functionality in cases of musculoskeletal and neurological complications.
Specific Treatment for Various Manifestations:
- Lyme Arthritis: Treatment may include non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) or corticosteroids in severe cases to reduce inflammation.
- Lyme Carditis: May require close cardiac monitoring and, in severe cases, temporary pacemaker implantation to control heart rhythm.
What are the complications that can arise from Lyme disease?
Lyme disease can lead to serious complications if not treated in time. These complications can affect various body systems and have long-term consequences. Here is a detailed description of the main complications that can arise from Lyme disease:
Neurological Complications:
- Facial Paralysis (Bell's Palsy): Temporary loss of muscle tone on one or both sides of the face.
- Lyme Meningitis: Inflammation of the meninges, causing severe headaches and neck stiffness.
- Radiculopathy: Intense pain, numbness, and muscle weakness due to inflammation of the nerve roots.
Cardiac Complications:
- Arrhythmias (Irregular Heartbeats): The heart may beat too fast, too slow, or irregularly, causing sensations of "fluttering" in the chest or fainting.
- Atrioventricular Block: Slowing or blocking of the heart's electrical signals, which may require the implantation of a pacemaker.
Musculoskeletal Complications:
- Lyme Arthritis: Chronic inflammation of the joints, most commonly the knees, causing severe pain and swelling.
Long-Term Complications:
- Lyme Encephalopathy: Cognitive problems, including confusion, memory loss, and difficulty concentrating.
- Peripheral Neuropathy: Damage to the peripheral nerves causing pain, numbness, and weakness in the hands and feet.
Other Complications:
- Post-Lyme Syndrome: Persistent and debilitating symptoms, such as pain, fatigue, and cognitive difficulties, that continue to affect patients long after antibiotic treatment. This chronic syndrome, similar to chronic fatigue syndrome and fibromyalgia, can severely impact quality of life in the long term.
Who Treats Lyme Disease?
Lyme disease is treated by specialists in infectious diseases, rheumatology, and, in some cases, neurology. These specialists have the expertise necessary to diagnose and manage this complex condition, which can affect various systems in the body. In Romania, some of the recognized doctors for treating Lyme disease include:
- Dr. Radu Mihail from Bucharest, an infectious disease specialist with extensive experience in diagnosing and treating tick-borne diseases.
- Dr. Maria Popescu from Cluj-Napoca, a rheumatologist known for her integrative approach to treating autoimmune and infectious conditions.
- Dr. Csep Andrei from Oradea, a rheumatologist with extensive experience in managing autoimmune and infectious conditions, including Lyme disease.
- Dr. Iulian Zaporojan from Oradea, a physician recognized for his skills in diagnosing and treating Lyme disease.
- Dr. Ana Ionescu from Iași, an infectious disease specialist known for her use of modern molecular diagnostic techniques.
- Dr. Cristian Băicuș from Timișoara, an infectious disease specialist with expertise in treating emerging and re-emerging diseases.
- Dr. Carmen Stoica from Oradea, an infectious disease specialist known for her meticulous approach to treating Lyme disease.
- Dr. Bogdan Cristian Ion from Târgu Mureș, a general practitioner known for his integrative approach to treating Lyme disease.
- Dr. Elena Vasilescu from Constanța, a neurologist who addresses the neurological complications of Lyme disease with exceptional expertise.
These doctors represent just a few examples of specialists dedicated to treating Lyme disease in Romania, each bringing their own approach and expertise to the field.
How Well is Lyme Disease Diagnosed?
The estimated percentage of undiagnosed Lyme disease can vary depending on sources and regions. Studies and reports suggest that a significant number of Lyme disease cases remain undiagnosed or misdiagnosed. In the United States, for example, the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) estimates that the actual number of Lyme disease cases could be up to 10 times higher than the number of officially reported cases. This would suggest that up to 90% of cases might be underdiagnosed.
In Europe, the situation may be similar, with significant regional variations. Some European studies suggest that underdiagnosis may be as frequent as in the United States, although specific data for each country varies.
These percentages indicate a substantial problem with underdiagnosis, highlighting the importance of medical education and public awareness to improve the recognition and reporting of this condition.
What are the Reasons for Underdiagnosis?
-
1. Non-Specific Symptoms: Symptoms of Lyme disease, such as fatigue, joint pain, fever, and headaches, are common to other conditions, which can lead to confusion with other illnesses and delay accurate diagnosis. -
2. Lack of Awareness: Both the public and some medical professionals may lack awareness about Lyme disease, its symptoms, and the risks associated with tick bites. This can lead to neglecting or underestimating the possibility of a Borrelia infection. -
3. Limited Testing: Diagnostic tests for Lyme disease, especially serological tests, may have limitations. Antibody tests can be false negative in the early stages of the disease, and PCR tests for bacterial DNA are not always available or accessible in all areas. -
4. Variety of Symptoms: Lyme disease can affect various body systems (neurological, cardiac, joint), making the symptoms very diverse and not always suggesting a single infectious cause. -
5. Late Presentation: Many patients do not remember being bitten by a tick or do not present the characteristic erythema migrans in the early stages, which delays recognition of the disease and seeking a diagnosis. -
6. Misdiagnosis: Sometimes, patients are misdiagnosed with other conditions (e.g., chronic fatigue syndrome, fibromyalgia, or autoimmune disorders) before it is determined that they have Lyme disease.
These issues contribute to the underdiagnosis of Lyme disease, leaving many patients without appropriate treatment for extended periods. Therefore, continuous medical education and increased public awareness are essential to improve the recognition and management of this condition.
Methods of Preventing Lyme Disease
Preventing Lyme disease involves a series of measures you can take to reduce the risk of being bitten by infected ticks:
1. Personal Protective Measures
Use insect repellents:
- What to use: Repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or IR3535 are effective. Apply these products to exposed skin and clothing. Permethrin repellents can be applied to clothing and gear as they kill ticks on contact. If using permethrin, apply it to your clothes a day before heading out to ensure it is effective and dry.
Wear appropriate clothing:
- How to dress: Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants. Light-colored clothing is preferred as ticks are easier to spot on it. Tuck the edges of your pants into your socks to prevent ticks from reaching your skin.
Check your body:
- What to do after outdoor activities: After spending time in high-risk areas, carefully inspect your entire body. Pay attention to hard-to-see areas such as the scalp, armpits, groin area, and the back of the knees. You can use a mirror to check all parts of your body. Also, check children and pets for ticks.
2. Environmental Management
- How to maintain your yard: Keep the lawn mowed short, remove excess leaves and vegetation, and create gravel or wood barriers between the lawn and wooded areas to reduce tick habitats. For example, if you have a house on the edge of a forest, regularly mow the lawn, remove fallen leaves, and place a gravel barrier between the yard and the forest to prevent tick migration.
- How to protect your pets: Use veterinarian-recommended antiparasitic products for dogs and cats to prevent tick infestations and bringing them into the house. For example, apply a monthly antiparasitic treatment to your dog and regularly check them for ticks, especially after walks in nature.
3. Education and Awareness
- Know the risk areas: Before going outdoors, learn about areas where ticks are common. Wooded regions, tall grass areas, and dense shrubs are places where ticks are often found. Check the county classification of Lyme disease cases in the national surveillance system. Based on data collected in 2022, it is advisable to avoid planning trips to Sibiu and Maramureș counties, as these regions reported significantly more Lyme disease cases than other counties.
-
Recognize ticks:
Ticks are small, brownish-black, and can be hard to spot, especially in their early stages (larva and nymph). They are usually the size of a poppy seed or a peppercorn.
Conclusion:
Lyme disease can be effectively treated if diagnosed early. The varied symptoms, ranging from skin rashes to neurological issues, can be managed with antibiotics and adjunctive therapies, such as hyperbaric oxygen therapy. Proper administration of antibiotics in the early stages of Lyme disease can eliminate the infection and prevent severe complications.
In advanced or persistent cases, additional therapies, such as hyperbaric oxygen therapy, can alleviate severe symptoms and speed up recovery. These treatments significantly contribute to reducing pain, inflammation, and neurological problems, allowing patients to resume their daily activities without long-term discomfort or limitations.




