Article reviewed by: Dr. Sturz Ciprian, Dr. Tîlvescu Cătălin and Dr. Alina Vasile
Article updated on: 21-04-2025
Hyperbaric therapy in post-traumatic stress disorder
- What is post-traumatic stress disorder?
- What are the causes of PTSD?
- How does PTSD manifest?
- What treatment options for PTSD exist?
- What is hyperbaric therapy?
- How can hyperbaric therapy help people with PTSD?
- What do studies say about using hyperbaric therapy in post-traumatic stress disorder?
- Benefits of hyperbaric therapy in treating post-traumatic stress
- How safe is hyperbaric therapy for those suffering from post-traumatic stress? Hyperbaric therapy, an aid in treating PTSD
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is one of the most debilitating mental conditions, affecting millions of people worldwide. Victims of violence, survivors of natural disasters, people who have gone through traumatic experiences, or war veterans may suffer from this disorder, which profoundly affects their quality of life. In the search for effective treatments, hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) has attracted the attention of researchers and doctors for its potential to alleviate PTSD symptoms.
What is post-traumatic stress disorder?
Post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD) is a severe psychological condition that occurs as a result of exposure to a traumatic event. According to the American Psychiatric Association, PTSD is characterized by persistent symptoms of anxiety, flashbacks, avoidance of situations associated with the trauma, and sleep disturbances.
Historically, PTSD has been documented since antiquity, being described in the accounts of soldiers who fought in ancient wars. For example, Herodotus mentions that an Athenian soldier from the Battle of Marathon (490 BC) went blind due to extreme stress, although he had not been physically injured. In the Roman Empire, physicians observed that legionnaires exhibited symptoms similar to those of PTSD after years of intense fighting. However, this disease was officially recognized as a psychiatric condition in the 1980s, following the experiences of Vietnam War veterans, and entered public consciousness as one of the most severe psychological conditions.
A study published in The Journal of Clinical Psychiatry showed that approximately 7-8% of people will experience PTSD at some point in their lives, and women are twice as likely as men to develop this disorder.
In Romania, post-traumatic stress is not indexed. But, in 2014 Silvia Florescu published a study conducted between 2025 and 2007 in which she talks about post-traumatic stress in Romania. According to this, 41.5% of Romanian respondents reported experiencing at least one traumatic event throughout their life. Of these, the lifetime prevalence of PTSD was 1.2%, and the prevalence in the last 12 months was 0.7%. The conditional risk of developing PTSD after exposure to a traumatic event was 4.7%.
What are the causes of PTSD?
Doctors and researchers agree that PTSD is the result of intense trauma, whether it's physical violence, sexual assault, serious accidents, natural disasters, or war experiences.
In children, PTSD can occur after physical or emotional abuse, and symptoms can affect their emotional development. According to the World Health Organization, children exposed to severe violence have an increased risk of developing PTSD and other psychological disorders.
For war veterans, PTSD is a frequent problem, often triggered by exposure to intense combat, loss of comrades, or extreme survival situations. A report by the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs shows that between 10% and 30% of war veterans suffer from PTSD.

How does PTSD manifest?
PTSD manifests through a series of specific symptoms, which are divided into four main categories:
- Reliving the trauma: Flashbacks, nightmares, and intense emotional reactions to memories of the traumatic event.
- Avoidance of stimuli associated with trauma: People avoid places, people, or situations that remind them of the event.
- Negative changes in thinking and mood: Feelings of guilt, emotional detachment, and loss of interest in pleasurable activities.
- Increased reactivity: Irritability, difficulty concentrating, insomnia, and exaggerated reactions to stimuli.
Given the multitude of triggering factors for PTSD, you can meet someone suffering from this syndrome at any time. If you notice these manifestations in someone, it's important to be empathetic, listen without judging, and recommend them to seek specialized help from a psychologist or psychiatrist.
What treatment options for PTSD exist?
Diagnosing PTSD involves a thorough psychiatric evaluation, according to DSM-5 criteria. Standard treatment includes cognitive-behavioral therapy, exposure therapy, and the use of antidepressant and anxiolytic medications.
In recent years, researchers have explored alternative therapies, such as transcranial magnetic stimulation, MDMA-assisted therapy, and hyperbaric therapy, all with promising results.
What is hyperbaric therapy?
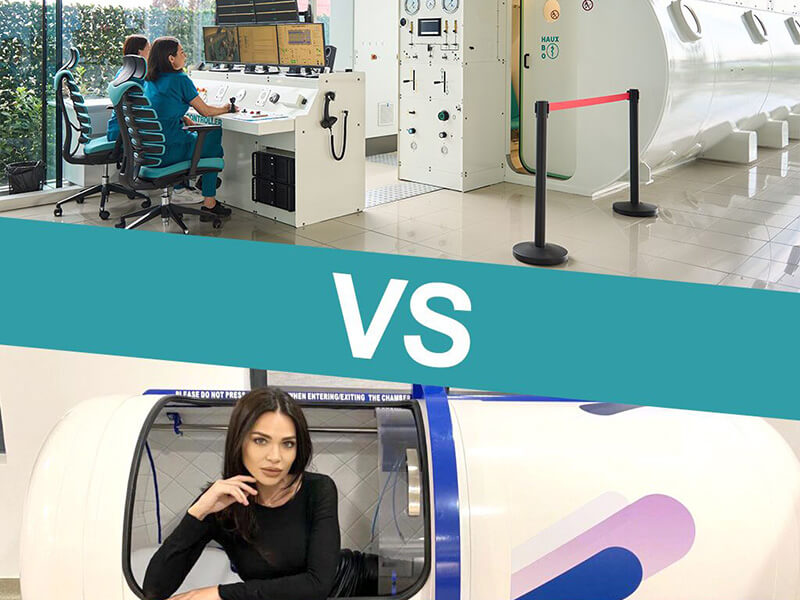
Hyperbaric therapy (HBOT) is a treatment method that involves inhaling pure oxygen in a special chamber, at a pressure higher than atmospheric pressure. This technique improves tissue oxygenation, stimulates cellular regeneration, and reduces inflammation. Initially used in emergency medicine, hyperbaric therapy has demonstrated benefits in treating brain injuries, vascular conditions, and neuropsychiatric disorders, including PTSD. Patients undergoing HBOT may experience cognitive, emotional, and physical improvements, making this therapy increasingly explored as an alternative option in modern medicine.
How can hyperbaric therapy help people with PTSD?
HBOT works by increasing the level of oxygen in the blood, reducing inflammation, and improving neuronal regeneration. Studies suggest that this therapy can help patients with PTSD through:
- Stimulating neuroplasticity: Hyperbaric therapy favors the reconnection and repair of affected neurons, thus improving the cognitive and emotional capacity of patients.
- Reducing brain inflammation: Inflammation plays a major role in PTSD symptoms. HBOT contributes to reducing levels of proinflammatory cytokines, such as IL-6 and TNF-alpha.
- Improving cerebral blood flow: Increased oxygenation helps better brain perfusion, reducing anxiety and depression.
- Improving sleep quality: Studies show that HBOT can contribute to reducing insomnia and nightmares associated with PTSD.
Through these effects, hyperbaric therapy represents a promising and complementary alternative to traditional treatments for PTSD, offering patients a real chance at recovery and improving their quality of life.
What do studies say about using hyperbaric therapy in post-traumatic stress disorder?
A study published in 2019 analyzed the impact of HBOT on veterans suffering from PTSD and traumatic brain injuries. The results were promising: patients reported a significant reduction in symptoms of anxiety, depression, and insomnia. Moreover, functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) showed normalized neuronal activity in brain regions affected by PTSD.
Another study, published in PMC, showed that HBOT had positive effects on patients with mild traumatic brain injuries, reducing cognitive and emotional symptoms associated with PTSD. These results suggest that HBOT could have a significant role in the treatment of PTSD, but additional studies are needed to confirm the efficacy and mechanisms involved.
Another study published in Journal of Neurotrauma showed that patients with PTSD and traumatic brain injuries had a significant improvement in symptoms after 40 sessions of HBOT. According to researchers, hyperbaric therapy "represents a promising method for reducing PTSD symptoms and improving patients' quality of life."
Benefits of hyperbaric therapy in treating post-traumatic stress
PTSD is often associated with neurobiological changes, including inflammation and oxidative stress at the brain level. These processes can lead to neuronal dysfunctions and clinical symptoms characteristic of PTSD. By reducing inflammation and oxidative stress, HBOT can contribute to restoring normal neuronal function and alleviating symptoms. Thus, patients suffering from PTSD who undergo regular sessions of hyperbaric therapy report numerous improvements.
- Reduction of anxiety and depression - Through its anti-inflammatory effect and by stimulating brain oxygenation, HBOT contributes to emotional regulation and reduction of depressive and anxious symptoms.
- Improvement of cognitive function - Many patients with PTSD experience memory and concentration deficits. Hyperbaric therapy stimulates cerebral blood circulation, facilitating cognitive functions.
- Sleep regulation - Insomnia and nightmares are common in people with PTSD. By reducing oxidative stress and improving the balance of neurotransmitters, HBOT promotes more restful sleep.
- Increased energy level - Improved oxygenation helps reduce chronic fatigue and increases patients' vitality.
- Amelioration of hypervigilance and emotional reactivity - HBOT can contribute to reducing exaggerated responses to stress stimuli and improving the ability to manage emotions.
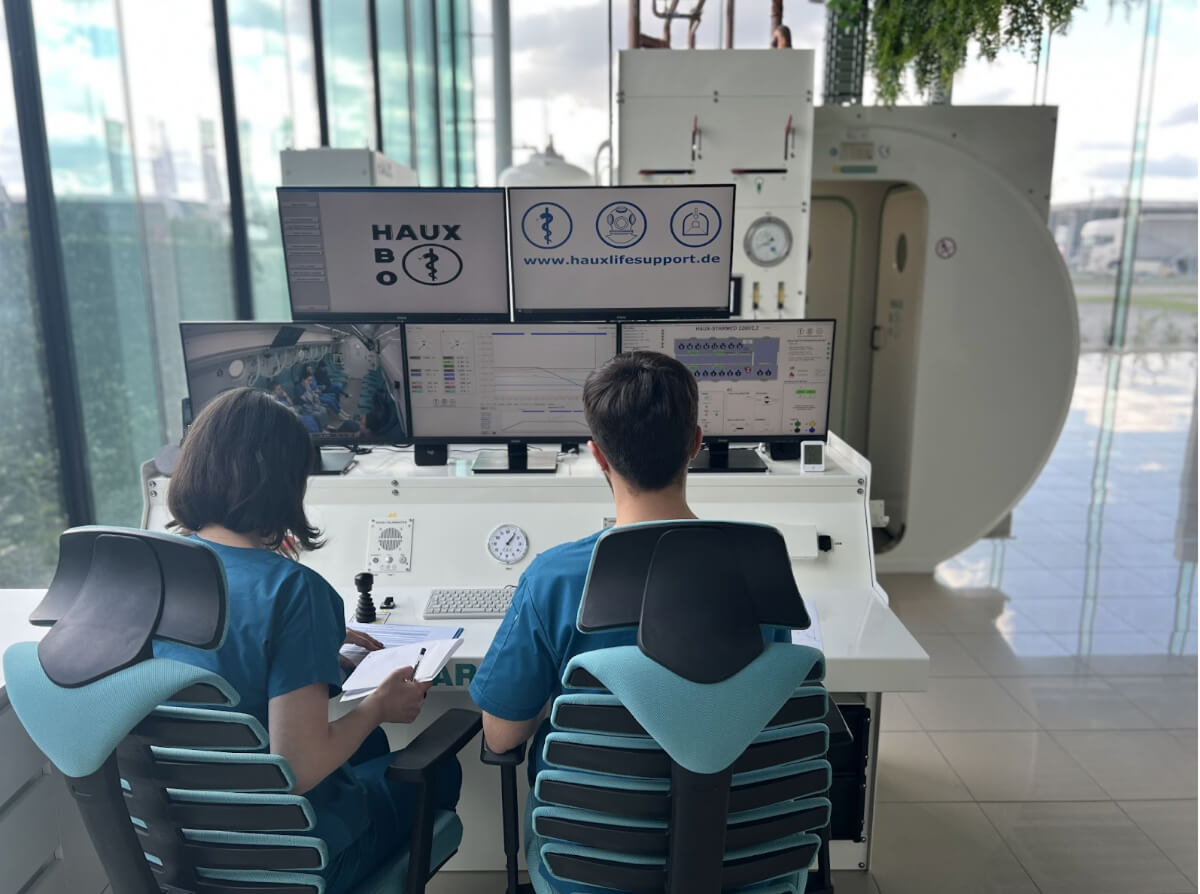

How safe is hyperbaric therapy for those suffering from post-traumatic stress?
Hyperbaric therapy is considered safe when administered under medical supervision in a controlled environment. Side effects are rare and usually minor, including discomfort in the ears or temporary fatigue. In extremely rare cases, more serious adverse effects may occur, such as barotrauma to the middle ear or oxygen toxicity.
It is essential that patients be evaluated before starting treatment to determine if they are suitable candidates for HBOT. Also, therapy must be carried out according to a protocol established by specialists to obtain the best results.
Hyperbaric therapy, an aid in treating PTSD
Hyperbaric therapy opens new horizons in the treatment of post-traumatic stress disorder, offering hope to those facing the debilitating effects of this condition. Current studies suggest that HBOT can become a catalyst for healing by reducing brain inflammation, stimulating neuroplasticity, and restoring patients' emotional balance. Although research is ongoing to refine and confirm these mechanisms, preliminary results provide an optimistic perspective on the future of this therapy.
For those living with PTSD and searching for effective solutions, hyperbaric therapy can represent a path to liberation and balance. Through the support of doctors, researchers, and those who believe in the power of healing, HBOT has the potential to become a reference treatment, offering patients not just symptom relief, but a real opportunity to rebuild their lives with confidence and hope.




